
AutomatedMLPack: A Python Package for End-to-End Automated Machine Learning
- Client or Institution: Internal / Random Project
- Project Goal: To streamline the end-to-end machine learning workflow—from data ingestion to evaluation and visualization—using a command-line-enabled Python package
- Tools Used: Python, Scikit-learn, Matplotlib, Seaborn, NumPy, Pandas, argparse
- Duration: 2 weeks
- Outcome: Fully functional and reusable Python package supporting classification and regression with CLI control
- Link: GitHub Repository
Command-Line Simplicity Meets Full-Stack ML Functionality
Abstract
AutomatedMLPack is a Python-based automation toolkit for machine learning that simplifies the data science pipeline. I built this package to support automated training and evaluation of multiple models on tabular datasets, using simple command-line arguments. The package includes modular scripts for ingestion, preprocessing, model training, performance comparison, and result visualization. Its CLI interface (run_train_pipeline.py) enables fast, repeatable experiments on classification or regression tasks with feature selection, model tuning, and logging.
🧠 Background & Problem Statement
Despite the growing demand for ML solutions, many workflows remain inefficient—requiring repetitive code and manual parameter tracking. The goal of this project was to automate key ML stages while keeping the interface accessible via a simple CLI.
The challenge was to design a package that is flexible for both beginners and experienced practitioners—supporting any tabular dataset, custom feature engineering, optional scaling, and advanced model benchmarking.
🗂 Dataset
- Heart Disease Classification Dataset
- Data Compatibility: Any structured/tabular dataset (CSV/TSV)
- Preprocessing Options:
- Standard scaling (optional)
- Train/test split (customizable)
- Feature selection using multiple strategies
- New feature engineering support
⚙️ Approach & Methodology
📁 Project Structure
The core codebase is organized in:
/modules/components: ingestion, transformation, and model training classes/utils: visualization functions and object serializationrun_train_pipeline.py: the CLI tool that orchestrates the workflow
🛠 Pipeline Features
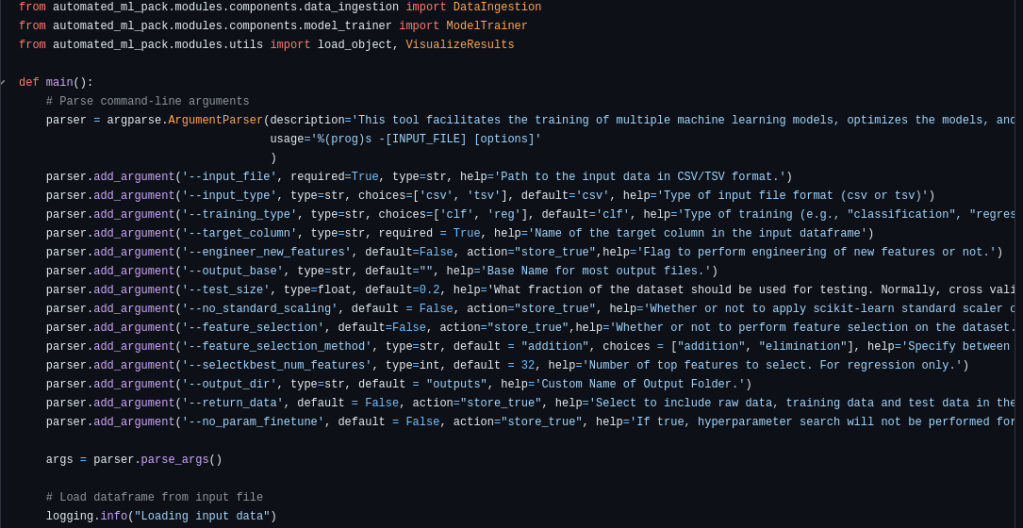
- Flexible CLI with argparse
Define input files, target column, model type, feature selection strategy, and more directly from the terminal.
- Modeling
Supports ensemble methods, boosting, neural nets, SVMs, logistic regression, and decision trees usingscikit-learn. - Feature Selection
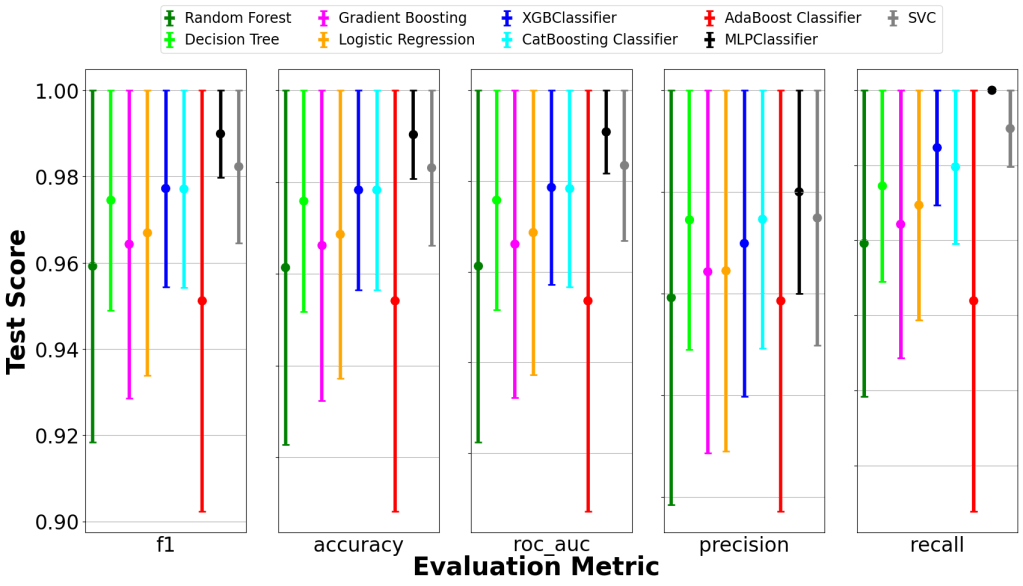
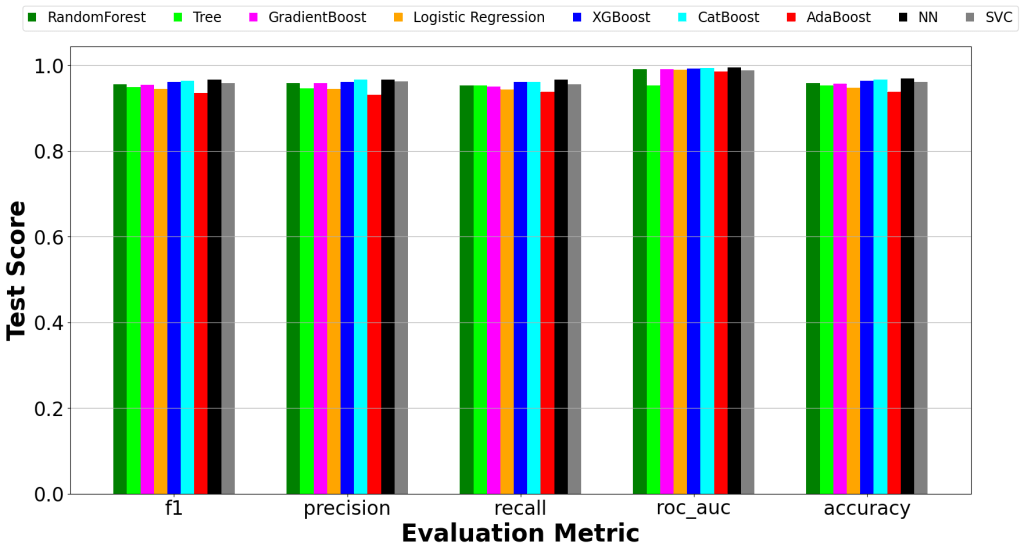
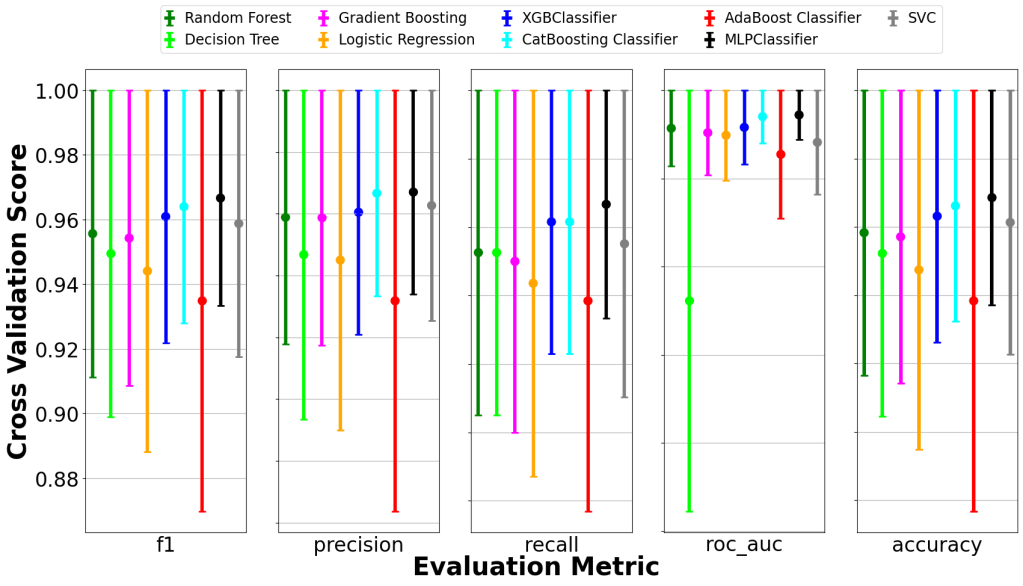
Offers 8 rankers and 13 aggregation methods for optimal subset selection. - Visualization
Generates comparative bar plots and error bars for model performance.
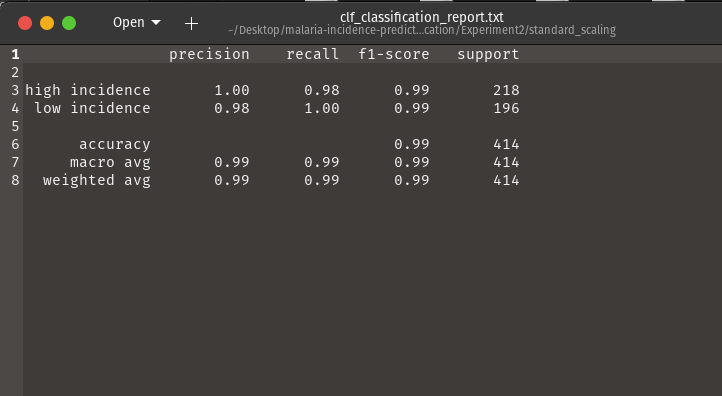
- Evaluation Reports
Generates.txtreports including precision, recall, F1, support, and accuracy for all classes.
📈 Key Results
- 📦 Built a reusable, installable Python library for automated ML
- 🧪 Enabled quick benchmarking across 10+ models
- 📊 Delivered plug-and-play visualizations and performance comparisons
- 🖥 CLI allows running complex experiments with a single command
💡 Lessons Learned / Innovations
- Implementing ensemble feature selection required handling different score scales, which was solved through robust scaling
- Learned to write clean, modular code compatible with
argparseand reusable for scripting - The CLI interface dramatically reduced experimentation time compared to manual scripting
💬 Discussion
AutomatedMLPack brings the principles of AutoML into a lightweight, customizable toolkit suited for research, hackathons, and rapid prototyping. It balances automation with flexibility, allowing users to override defaults and control how their pipeline behaves.
The ability to quickly test multiple models, visualize outcomes, and export reports—without writing redundant code—marks a major productivity boost.
📣 Call to Action
This was a self-initiated project aimed at improving machine learning productivity. If you’re building ML pipelines or teaching ML to students, check out the repo or start a conversation.
🔭 Final Thoughts & Future Directions
There’s great potential to extend this tool:
- Add Docker support for containerized experiments
- Introduce hyperparameter search grids with cross-validation
- Extend support for deep learning via TensorFlow or PyTorch
- Integrate streamlit or Gradio as a web interface wrapper


Leave a comment